Emergency Backup Power Units for Hospitals and Healthcare
Aug 15,2025
In the healthcare industry, an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) is more than just a convenience. It’s a lifeline for ensuring patient safety, protecting sensitive equipment, and maintaining essential operations. Without a reliable power supply, hospitals can face serious patient safety risks, especially during emergencies and power outages.
Hospitals widely use backup generators to maintain operations during crises, natural disasters, or unexpected power outages. This article explores why backup power is crucial for hospitals, the types of generators used, and how healthcare facilities can ensure their power generation systems are always ready when needed.
Why Hospital Backup Power Is a Lifeline?
Critical Operations Depend on Continuous Power
When it comes to healthcare, downtime is not an option. Hospitals operate around the clock, with life-support systems, surgical suites, diagnostic equipment, and intensive care units all depending on a continuous supply of electricity. A sudden blackout can endanger lives within minutes, making emergency generators for hospitals essential.
Supporting All Aspects of Hospital Function
The hospital’s power supply ensures the normal operation of critical medical equipment, from ventilators to heart monitors. The medical facility’s backup generators also support lighting, HVAC systems, electronic medical records, and communication tools.
The Importance of Backup Power in Healthcare Facilities
Healthcare facilities require continuous power to support their operations. Even a brief outage can compromise patient safety, lead to equipment damage, or interrupt surgeries. Therefore, backup generators for healthcare facilities are not just a regulatory requirement—they are essential for survival.
Risks of Power Outages in Healthcare
A power generator for hospital operations provides resilience during severe storms, earthquakes, or widespread grid failures. Without such systems, patients and staff may be left vulnerable, and life-saving procedures could be interrupted.
Regulatory Requirements
In many cases, federal and state regulations mandate that hospitals must have reliable emergency generators. These regulations ensure that hospitals can continue life-saving procedures without delay.
Critical Areas Requiring Backup Power
Operating rooms, intensive care units, and emergency departments all require guaranteed access to electricity, which is only possible with robust hospital backup generator systems.
How Many Generators Does a Hospital Need?
Determining Hospital Generator Requirements
The number of generators a hospital requires depends on its size, capacity, and patient load. Larger hospitals typically operate multiple hospital generators to ensure redundancy. Redundant systems mean that if one generator fails, others can seamlessly take over without disrupting operations.
Considerations for Smaller Facilities
For smaller healthcare facilities, a single generator for hospital use might suffice, but it must be powerful enough to support essential operations. The calculation often considers the hospital’s peak load demand and critical equipment requirements. In most cases, emergency generators for hospitals are sized to support critical systems rather than the entire facility, ensuring that life-saving equipment always receives priority.
How to Prepare a Generator for an Emergency
Importance of Preparedness
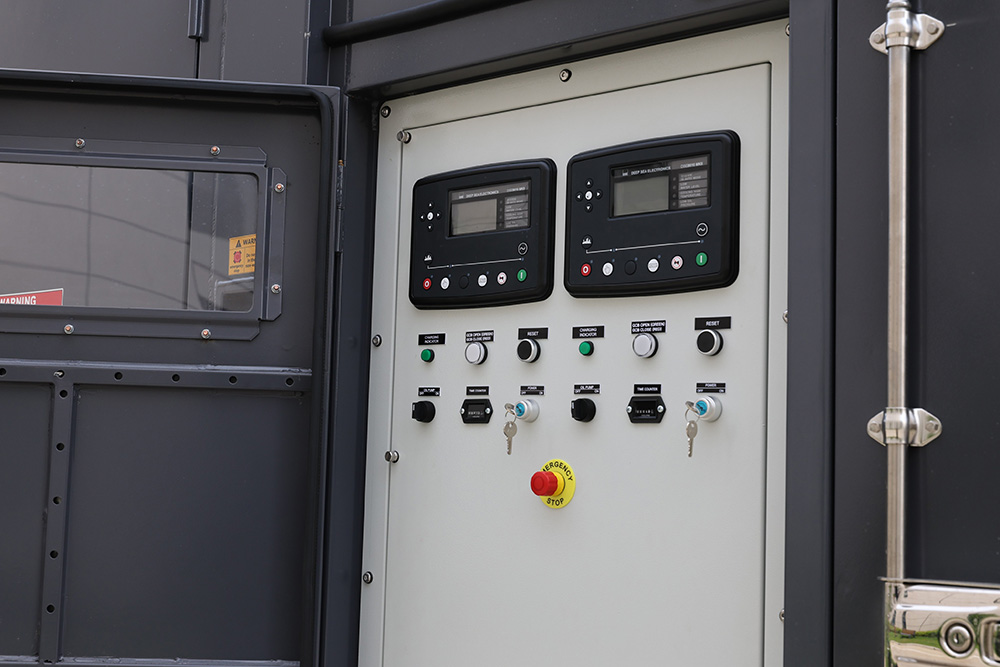
Preparedness is critical in the healthcare industry. Simply having backup generators for healthcare facilities is not enough—they must be ready to operate instantly during any unexpected outage. Hospitals should implement comprehensive protocols to keep their generators fully operational and responsive at all times.
Steps to Ensure Generator Readiness
Preparing a hospital backup generator involves multiple steps. Conducting routine load tests helps confirm the generator can handle critical power demands. Ensuring an adequate fuel supply, whether for diesel generators for hospitals or natural gas alternatives, prevents operational interruptions.
Staff training on emergency protocols ensures personnel can react quickly and correctly. Regular inspection of transfer switches, electrical connections, and control systems helps identify potential problems before they escalate. Maintaining detailed logs of all maintenance and tests supports accountability and compliance with safety standards.
Benefits of Proactive Preparation
Proactive preparation reduces the likelihood of generator failure during emergencies, allowing the hospital generator to respond immediately and reliably. By embedding these practices into standard operational procedures, hospitals can protect patient safety, maintain essential services, and ensure continuity of care even during severe power disruptions.
Generator Fuel Sources
The choice of fuel for a hospital generator is crucial. The main types of generators and their characteristics can be summarized in the table below:
| Generator Type | Key Features | Advantages | Considerations |
| Diesel Generators for Hospitals | Reliable and high-energy density | Delivers high power output quickly; ideal for emergency use | Requires on-site fuel storage; emissions concerns |
| Natural Gas Generators | Cleaner-burning alternative | Reduces emissions; no need for on-site fuel storage | Dependent on utility infrastructure; may fail if gas supply is interrupted |
| Dual-Fuel Systems | Uses both diesel and natural gas | Provides resilience and fuel flexibility | Requires more complex maintenance and higher initial cost |
Fuel strategy is part of an overall generation solution that allows hospitals to operate independently of the grid. It includes considerations like fuel storage, switching between fuel types, system integration, and monitoring tools to track consumption and performance, supporting continuous operations and adapting to emergencies.
Power Generation Systems for Oil and Gas
Oil Industry Power Systems
Power generation systems in the oil industry are critical for extraction, refining, and distribution operations. They provide reliable electricity to pumps, drilling rigs, and control systems, ensuring operational continuity.
These systems are designed for high capacity and redundancy to handle remote and hazardous environments, where any downtime can lead to costly production losses and safety risks.
Gas Industry Power Systems
In the natural gas sector, power generation systems support compressors, processing plants, and pipeline operations. They are tailored to maintain stable power under fluctuating demand and extreme conditions. Reliability, efficiency, and backup capabilities are essential to prevent interruptions that could compromise safety and gas supply.
Lessons from Healthcare Generators
Insights from the healthcare industry generators often inform both oil and gas power systems. Hospitals’ experience with backup generators helps guide effective fuel management, emergency preparedness, and system resilience in these energy sectors.
Generator Testing and Maintenance Requirements
Backup generators for healthcare facilities are effective only when maintained carefully, with regular inspections, performance testing, and prompt repairs to prevent unexpected failures and ensure a continuous power supply during emergencies.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
The healthcare industry follows strict standards for testing and upkeep to ensure consistent performance and compliance with safety regulations. Without proper attention, even minor issues can escalate and jeopardize hospital operations.
Key Maintenance Activities
Maintenance involves regular testing under load conditions to verify operational readiness. Periodic inspections of electrical systems, fuel supply, and transfer switches help identify potential issues early. Annual full-load testing simulates real emergency conditions, while scheduled servicing of filters, lubricants, and batteries ensures the generator stays in peak condition.
Record-Keeping and Reliability
Splitting these tasks into dedicated checks and keeping careful maintenance records reduces the chance of generator failure. Detailed documentation helps ensure reliable operation during critical moments and supports compliance with regulatory standards.
Generator Location
Where a hospital places its generators is just as important as having them. Poorly located emergency generators for hospitals can fail if exposed to flooding, fire hazards, or restricted ventilation. Hospitals should install generators above flood levels and ensure adequate ventilation and exhaust clearance.
It is also important to secure generators in protected enclosures to withstand extreme weather and to place fuel tanks in safe, accessible areas. By carefully planning generator placement in this way, hospitals enhance the reliability of their power generation systems.
How to Choose the Right Power Generation System for Your Hospital
Selecting the right power generation solution involves evaluating your facility’s unique needs. Hospitals should consider:
- Capacity requirements– Calculate the power needed for critical equipment and systems.
- Redundancy– Implement multiple hospital generators to ensure backup coverage.
- Fuel type– Decide between diesel generators for hospitals, natural gas, or hybrid solutions.
- Compliance– Ensure generators meet local, state, and federal regulations.
- Scalability– Choose systems that can grow with hospital expansion.
- Integration– Ensure compatibility with existing power distribution systems.
Healthcare industry generators must be reliable, scalable, and compliant with stringent healthcare standards. Working with trusted power generation system providers helps hospitals design a solution tailored to their needs.
Beyond Healthcare: Battery Systems
Application in Other Sectors
While hospitals have the most critical need for reliable backup power, similar principles apply to battery systems in other sectors.
Advantages and Limitations
Advanced battery systems offer immediate, quiet, and low-maintenance power, making them ideal for short-term outages and rapid response scenarios.
They require careful monitoring and regular maintenance to ensure efficiency and reliability. Batteries have limitations, including lower capacity compared to generators, potential degradation over time, and the need for temperature-controlled environments.
Integration with Generators
By understanding these advantages and disadvantages, organisations can design battery systems that complement traditional backup generators, ensuring a continuous and resilient power supply in various settings.
Conclusion
Reliable power generation is a critical component of hospital operations, with backup generators and diesel systems designed to ensure safety, reliability, and regulatory compliance.
Proper planning, routine maintenance, and strategic placement are essential for these systems to function when needed, and investing in dependable power solutions allows healthcare facilities to maintain continuous operations and support patient care even during outages, underscoring how essential hospital generators are for maintaining uninterrupted healthcare services.
--- END ---